Climate phenomena are becoming increasingly extreme. Intense heat waves, melting glaciers, rising sea levels, the extinction of various species, increased rainfall in some regions, and prolonged droughts in others are just a few of the disasters we currently face.
One of the main drivers of these changes is global warming, caused by the accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O). These gases trap the sun’s heat, preventing it from escaping back into space, resulting in rising global average temperatures and disrupting the climate system.
Human activity, especially the use of fossil fuels like oil, gas, and coal to power homes, factories, and transportation, is one cause of this phenomenon.
To reduce greenhouse gas emissions and balance the remaining emissions by absorbing an equivalent amount from the atmosphere, many countries are committed to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050.
WHAT IS THE CARBON CYCLE
Carbon is one of the most abundant elements in the universe, present in various forms such as graphite and diamond. It can bond with other chemical elements, forming numerous compounds. In the human body, carbon represents about 20% of the composition.
When carbon bonds with two oxygen atoms, it forms carbon dioxide (CO2), a molecule essential in the cycles of cellular respiration and plant photosynthesis.
In the environment, there are two types of carbon cycles:
The Biogenic Carbon Cycle ensures the circulation of this element through the environment and living organisms. Photosynthesis and respiration are essential processes in this cycle. It begins with plants and organisms that absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to perform photosynthesis, converting it into oxygen and sugar (such as glucoses), which the plant uses to grow. When animals and plants consume glucose, carbon dioxide is emitted back into the atmosphere through respiration, making it available for a new photosynthesis cycle.
The Non-Biogenic Carbon Cycle, also known as the geological carbon cycle, regulates the movement of carbon through the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and lithosphere. Carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere dissolves in rainwater, forming carbonic acid (H2CO3), facilitating rock erosion. This weathering releases Ca2+ and HCO3- ions, which can be carried to the ocean and used by marine organisms to form shells. When these organisms die, their shells settle on the ocean floor, accumulating as sediments. Over time and pressure, these sediments can turn into fossil fuel deposits and rocks.
Here is an example of how the Carbon Cycle works:

Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, impact both carbon cycles. By extracting carbon from fossil deposits faster than the cycle can absorb, we increase CO2 concentrations in the atmosphere, contributing to global warming.
THE IMPORTANCE OF THE CARBON CYCLE
The carbon cycle, or carbon recycling, is essential for the survival of our planet. Among its leading roles, the following stand out:
- Structure of Organic Molecules: Carbon is a fundamental element in the composition of organic molecules, which are the basis of life on Earth as we know it.
- Climate Regulation: The carbon cycle is directly linked to climate regulation and maintaining the planet’s stability. Alterations in this cycle can have severe environmental consequences, such as the increase in the greenhouse effect and climate change.
- Photosynthesis and Respiration: Photosynthesis and respiration are essential for the carbon cycle. In photosynthesis, autotrophic photosynthetic organisms remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and release oxygen, which other living beings use in respiration.
- Carbon Recycling: The carbon cycle is a biogeochemical cycle that ensures carbon recycling, allowing this element to interact with the environment and living organisms.
- Ecological Balance: The carbon cycle maintains the balance of the climate and the biodiversity of Earth. Life on Earth exists only because of this natural phenomenon.
THE ROLE OF COMPANIES IN PLANETARY SUSTAINABILITY
Companies play a crucial role in promoting sustainability and building a greener future. They can make a difference by adopting sustainable practices and raising awareness about their importance.
People are increasingly concerned about the environment, which is reflected in their consumption habits, especially in food and pet products. Consumers value transparency in sourcing ingredients and prefer brands that limit their environmental impact.
According to a report by Mintel (Patent Insights: Innovations Shaping Pet Food, 2022), 71% of U.S. consumers who purchase pet supplies are interested in items made with eco-friendly materials or practices.
Additionally, 58% of pet food buyers in Germany want to know more about the environmental footprint of different pet foods.
Similarly, food and beverage consumers in the U.S. also value tangible and relatable factors, such as recyclability and minimizing food waste, when making their purchasing decisions, as highlighted by Mintel’s research (Sustainability in Food and Drink – U.S. – 2023).
In summary, consumers are increasingly concerned with sustainability in both pet food and the food and beverage sector. However, the practical implementation of these initiatives and effective communication remain significant challenges for brands.
Companies are adopting ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) practices to meet this market and environmental demand. ESG represents a set of best practices in business management related to environmental, social, and governance factors.
Evaluation criteria assess organizations’ commitment to ESG and include aspects such as natural resource management, equity and inclusion, and transparency and ethics. These criteria go beyond incorporating sustainable practices and reflect a broader commitment to integrity, accountability, and positive impact on society.
Another essential action is the transparency of the carbon footprint, which encompasses emissions from direct operations (such as energy consumption and transportation) and those associated with indirect activities (such as raw material production, product manufacturing, and goods transportation).
Therefore, carbon offsetting becomes essential. This is a process through which companies neutralize their carbon emissions by investing in projects that reduce or remove equivalent amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. By offsetting their emissions, organizations take responsibility for the environmental impact of their operations.
These actions help companies evaluate and reduce their environmental impact, contributing significantly to the fight against climate change.
THE CARBON CYCLE AT BIORIGIN
Understanding the need to actively contribute to the well-being of people, animals, and the environment, Biorigin promotes actions to reduce its environmental impact. The company ensures traceability, sustainability, and quality throughout production, from raw material (sugarcane produced by Zilor) to the final product. Additionally, it uses 100% renewable sources for electricity and thermal energy (steam).
In 2023, Biorigin’s direct greenhouse gas emissions (Scopes 1, 2, and 3) across its three units totaled 22,195.23 tons of carbon dioxide (CO₂), equivalent to an emission of 0.67 kg of CO₂ per kg of dry product, considering Scopes 1, 2, and 3, from production to the port of destination.
This information is based on greenhouse gas inventories validated by a third party in compliance with the GHG Protocol. (*This is not a life cycle analysis.) Our emissions boundary covers everything from the transportation of chemicals and raw materials to industrial production, internal logistics, transportation between warehouses, and transportation to the destination port.
Biorigin operates with two carbon cycles: the biogenic and the non-biogenic.
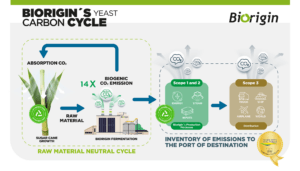
The Biogenic Carbon Cycle comes from the fermentation of sugarcane, the raw material used to produce yeast and yeast extract. During manufacturing, biogenic CO2 is released and later absorbed by the sugarcane plantation, forming a neutral cycle for the raw material.
On the other hand, the Non-Biogenic Carbon Cycle is related to using fossil fuels in transportation, which is part of Biorigin’s industrial processes and global distribution. For the eighth consecutive year, Biorigin has held the Gold Seal in the Brazilian GHG Protocol Program for disclosing the emissions inventory for Scopes 1 and 2, verified by a third party by ISO 14064-3:2007 (SGS).
More than 93% of the carbon emitted in Biorigin’s process is biogenic. In 2023, 326,410.395 tons of biogenic CO₂ were emitted, which nature will capture in the next sugarcane growth cycle.
Check out Biorigin’s Carbon Cycle diagram:
The company also promotes the maintenance of management system certifications at its Brazilian units:

To reinforce our commitment to transparency and socio-environmental responsibility, we publish the Annual Sustainability Report, highlighting the key results of the 2022/2023 harvest. This report addresses business-related topics and environmental, social, and governance aspects, including climate change and innovation. To read the report highlights, click here.
“Biorigin’s emissions reflect a positive path about climate change. Our largest emission comes from the biogenic cycle, which reinforces using renewable sources (biomass) for energy and steam generation in the production process. Our ingredients have low emissions, considering the data from inventories validated by a third party. Although there is a long way to go in combating climate change and transitioning to renewable energy, Biorigin is advanced in this area, with more than 90% of our energy coming from renewable sources,” says Walter José Sarno Santos, Environmental Coordinator at Biorigin.
MEET BIORIGIN
For over 20 years, Biorigin has specialized in biotechnological processes, producing natural-origin ingredients for human food, pet food, and livestock feed. The company also maintains a strong commitment to sustainability and respect for the environment.
Therefore, it is essential that companies and consumers participate in this movement. This includes concern for the source of raw materials and the food present in every meal. Biorigin, committed to these principles, continues to work towards a more sustainable and healthier future for everyone.








